GraphQL API
The GraphQL API allows performing queries and mutations to interact with the content-types through Strapi's GraphQL plugin. Results can be filtered, sorted and paginated.
To use the GraphQL API, install the GraphQL plugin:
- Yarn
- NPM
yarn add @strapi/plugin-graphql
npm install @strapi/plugin-graphql
Once installed, the GraphQL playground is accessible at the /graphql URL and can be used to interactively build your queries and mutations and read documentation tailored to your content-types:
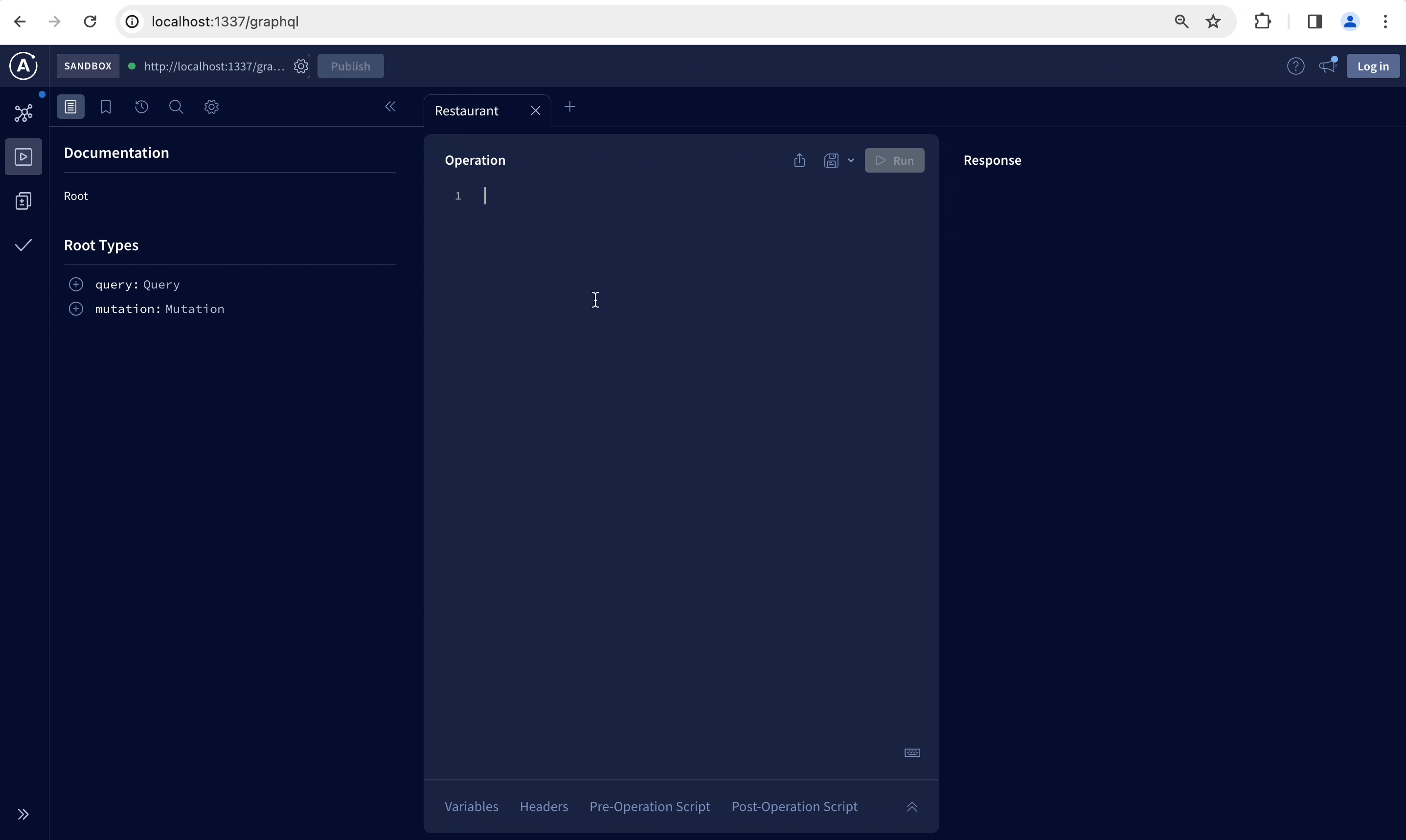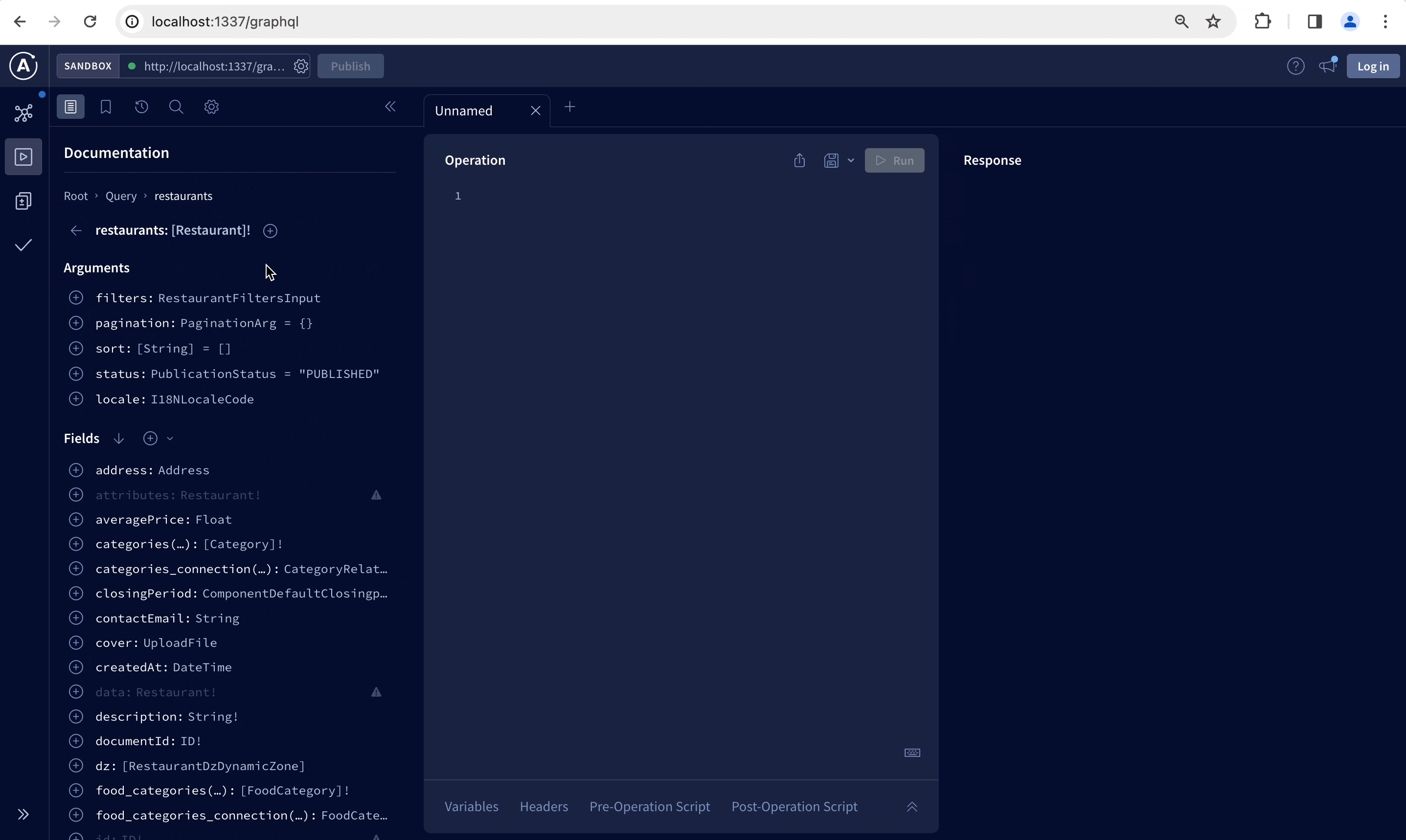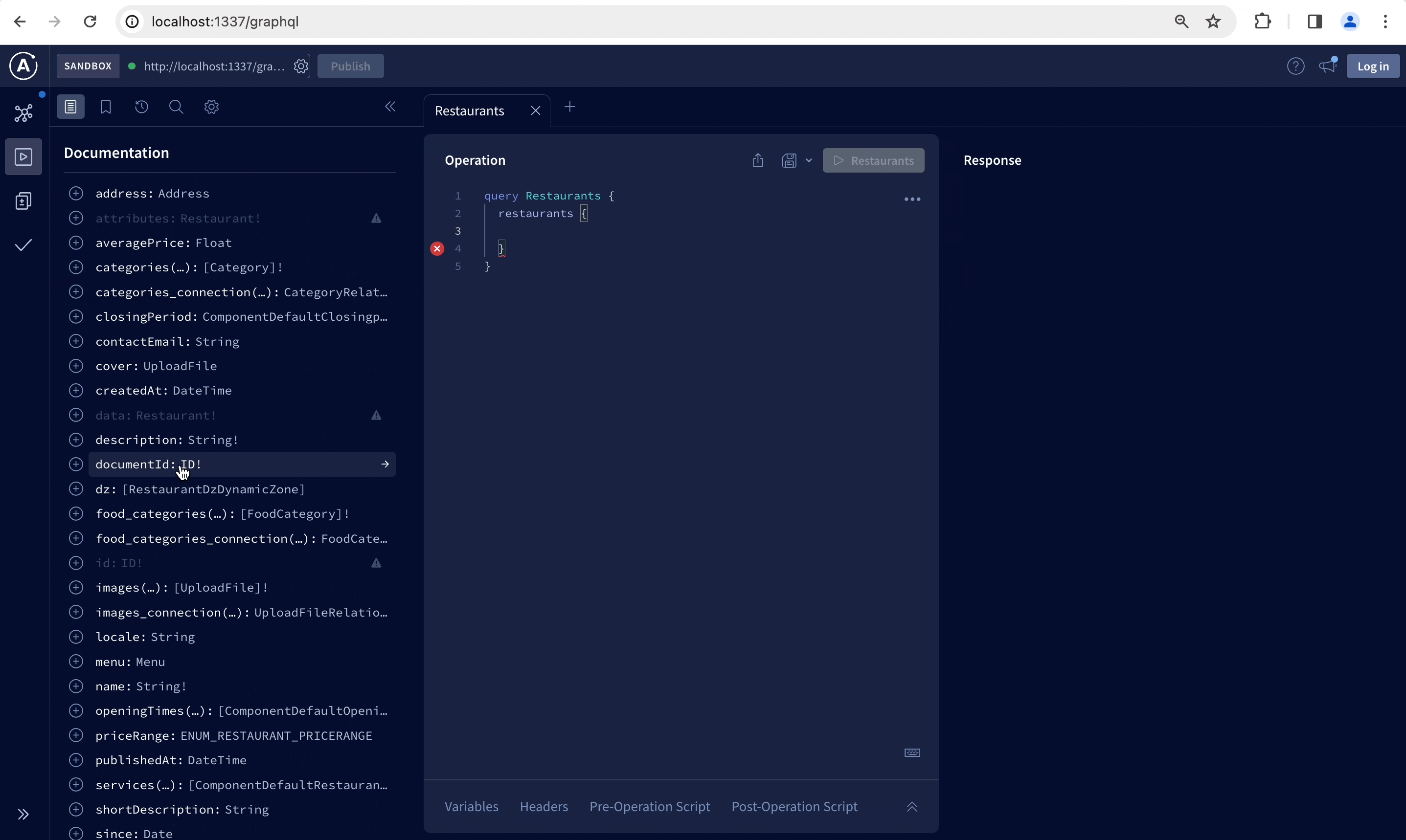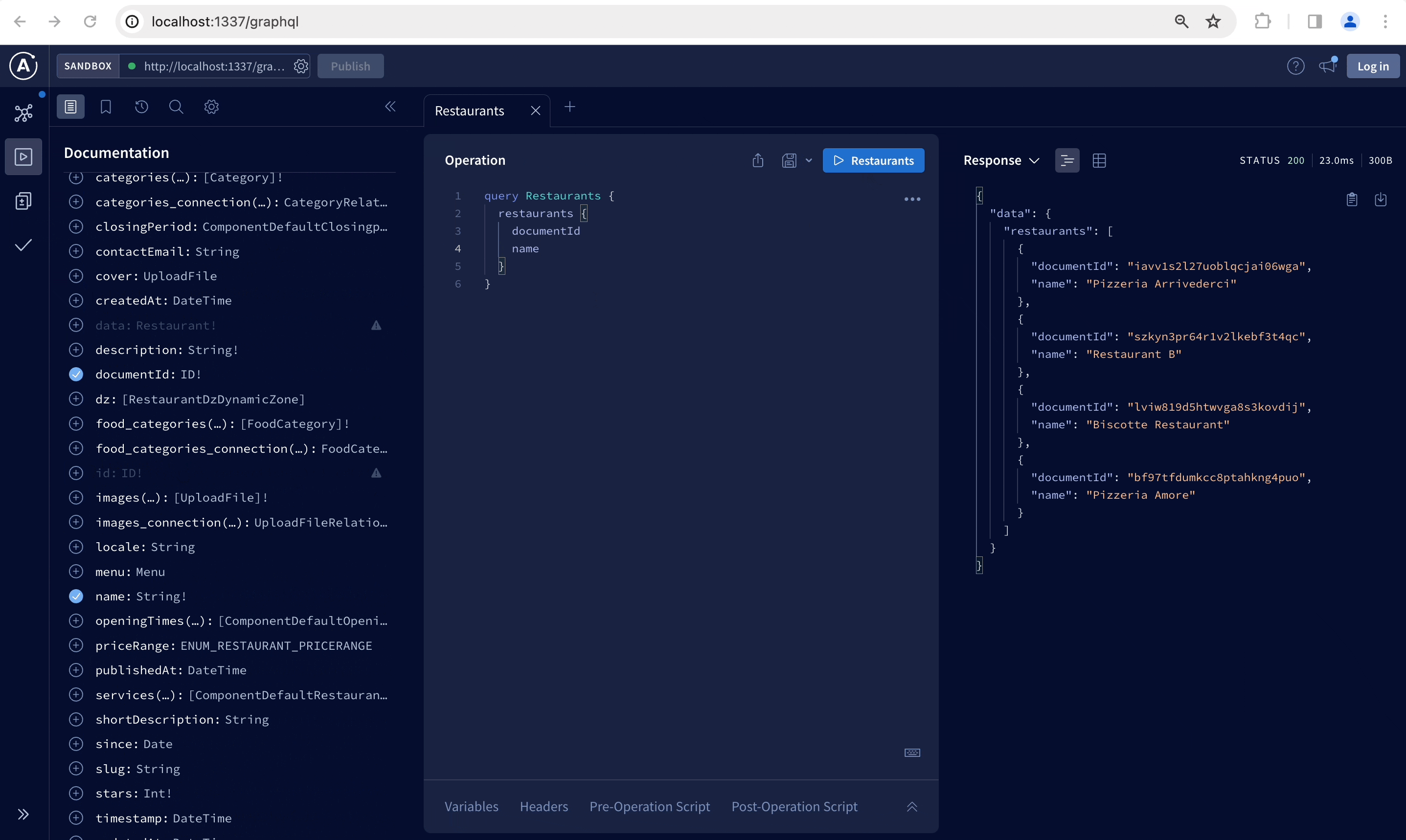
The GraphQL API does not support media upload. Use the REST API POST /upload endpoint for all file uploads and use the returned info to link to it in content types. You can still update or delete uploaded files with the updateUploadFile and deleteUploadFile mutations using media files id (see mutations on media files).
Queries
Queries in GraphQL are used to fetch data without modifying it.
When a content-type is added to your project, 2 automatically generated GraphQL queries are added to your schema, named after the content-type's singular and plural API IDs, as in the following example:
| Content-type display name | Singular API ID | Plural API ID |
|---|---|---|
| Restaurant | restaurant | restaurants |
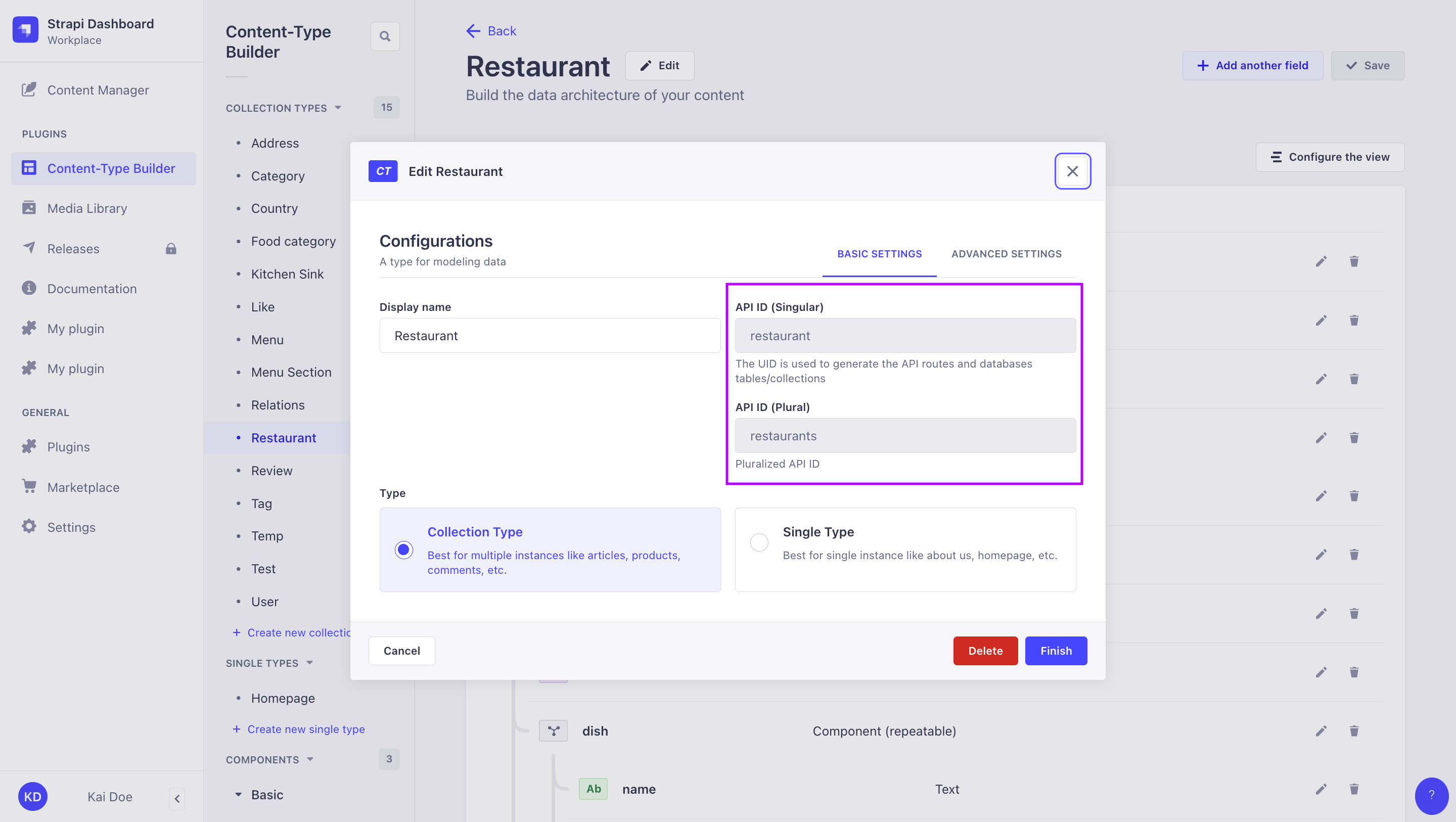
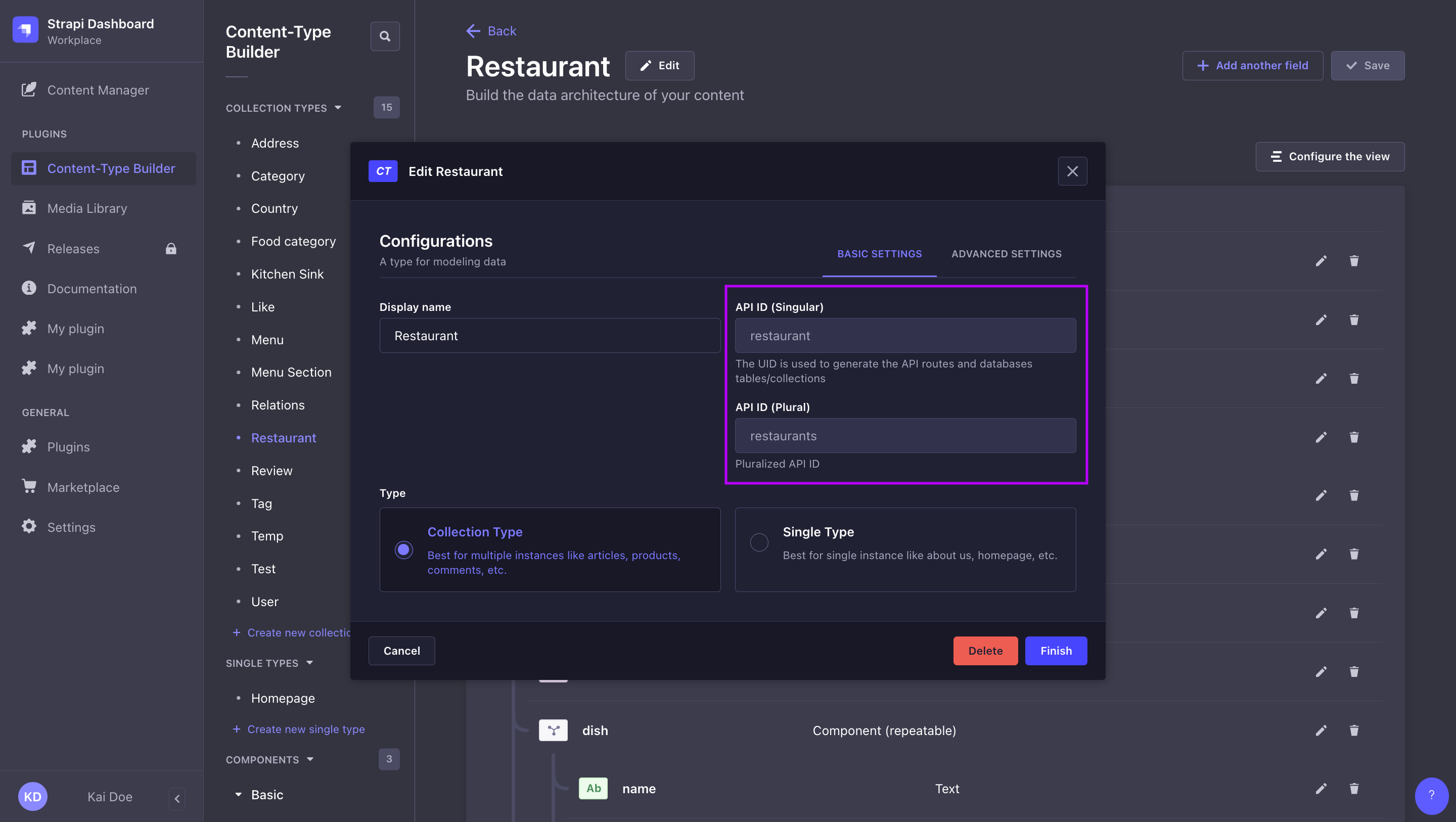
Singular API ID vs. Plural API ID:
Singular API ID and Plural API ID values are defined when creating a content-type in the Content-Type Builder, and can be found while editing a content-type in the admin panel (see User Guide). You can define custom API IDs while creating the content-type, but these can not modified afterwards.
Fetch a single document
Documents can be fetched by their documentId.
{
restaurant(documentId: "a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl") {
name
description
}
}
Fetch multiple documents
To fetch multiple documents you can use simple, flat queries or Relay-style queries:
- Flat queries
- Relay-style queries
To fetch multiple documents you can use flat queries like the following:
restaurants {
documentId
title
}
Relay-style queries can be used to fetch multiple documents and return meta information:
{
restaurants_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
pageInfo {
pageSize
page
pageCount
total
}
}
}
Fetch relations
You can ask to include relation data in your flat queries or in your Relay-style queries:
- Flat queries
- Relay-style queries
The following example fetches all documents from the "Restaurant" content-type, and for each of them, also returns some fields for the many-to-many relation with the "Category" content-type:
{
restaurants {
documentId
name
description
# categories is a many-to-many relation
categories {
documentId
name
}
}
}
The following example fetches all documents from the "Restaurant" content-type using a Relay-style query, and for each restaurant, also returns some fields for the many-to-many relation with the "Category" content-type:
{
restaurants_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
description
# categories is a many-to-many relation
categories_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
}
}
pageInfo {
page
pageCount
pageSize
total
}
}
}
For now, pageInfo only works for documents at the first level. Future implementations of Strapi might implement pageInfo for relations.
Possible use cases for pageInfo:
This works:
{
restaurants_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
description
# many-to-many relation
categories_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
}
}
pageInfo {
page
pageCount
pageSize
total
}
}
}
This does not work:
{
restaurants_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
description
# many-to-many relation
categories_connection {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
# not supported
pageInfo {
page
pageCount
pageSize
total
}
}
}
pageInfo {
page
pageCount
pageSize
total
}
}
}}
Fetch media fields
Media fields content is fetched just like other attributes.
The following example fetches the url attribute value for each cover media field attached to each document from the "Restaurants" content-type:
{
restaurants {
images {
documentId
url
}
}
}
For multiple media fields, you can use flat queries or Relay-style queries:
- Flat queries
- Relay-style queries
The following example fetches some attributes from the images multiple media field found in the "Restaurant" content-type:
{
restaurants {
images_connection {
nodes {
documentId
url
}
}
}
}
The following example fetches some attributes from the images multiple media field found in the "Restaurant" content-type using a Relay-style query:
{
restaurants {
images_connection {
nodes {
documentId
url
}
}
}
}
For now, pageInfo only works for documents. Future implementations of Strapi might implement pageInfo for the media fields _connection too.
Fetch components
Components content is fetched just like other attributes.
The following example fetches the label, start_date, and end_date attributes values for each closingPeriod component added to each document from the "Restaurants" content-type:
{
restaurants {
closingPeriod {
label
start_date
end_date
}
}
}
Fetch dynamic zone data
Dynamic zones are union types in GraphQL so you need to use fragments (i.e., with ...on) to query the fields, passing the component name (with the ComponentCategoryComponentname syntax) to __typename:
The following example fetches data for the label attribute of a "Closingperiod" component from the "Default" components category that can be added to the "dz" dynamic zone:
{
restaurants {
dz {
__typename
...on ComponentDefaultClosingperiod {
# define which attributes to return for the component
label
}
}
}
}
Fetch draft or published versions
If the Draft & Publish feature is enabled for the content-type, you can add a status parameter to queries to fetch draft or published versions of documents :
query Query($status: PublicationStatus) {
restaurants(status: DRAFT) {
documentId
name
publishedAt # should return null
}
}
query Query($status: PublicationStatus) {
restaurants(status: PUBLISHED) {
documentId
name
publishedAt
}
}
Mutations
Mutations in GraphQL are used to modify data (e.g. create, update, and delete data).
When a content-type is added to your project, 3 automatically generated GraphQL mutations to create, update, and delete documents are added to your schema.
For instance, for a "Restaurant" content-type, the following mutations are generated:
| Use case | Singular API ID |
|---|---|
| Create a new "Restaurant" document | createRestaurant |
| Update an existing "Restaurant" restaurant | updateRestaurant |
| Delete an existing "Restaurant" restaurant | deleteRestaurant |
Create a new document
When creating new documents, the data argument will have an associated input type that is specific to your content-type.
For instance, if your Strapi project contains the "Restaurant" content-type, you will have the following:
| Mutation | Argument | Input type |
|---|---|---|
createRestaurant | data | RestaurantInput! |
The following example creates a new document for the "Restaurant" content-type and returns its name and documentId:
mutation CreateRestaurant($data: RestaurantInput!) {
createRestaurant(data: {
name: "Pizzeria Arrivederci"
}) {
name
documentId
}
}
When creating a new document, a documentId is automatically generated.
The implementation of the mutations also supports relational attributes. For example, you can create a new "Category" and attach many "Restaurants" (using their documentId) to it by writing your query like follows:
mutation CreateCategory {
createCategory(data: {
Name: "Italian Food"
restaurants: ["a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl", "bf97tfdumkcc8ptahkng4puo"]
}) {
documentId
Name
restaurants {
documentId
name
}
}
}
If the Internationalization (i18n) feature is enabled for your content-type, you can create a document for a specific locale (see i18n documentation).
Update an existing document
When updating an existing document , pass the documentId and the data object containing new content. The data argument will have an associated input type that is specific to your content-type.
For instance, if your Strapi project contains the "Restaurant" content-type, you will have the following:
| Mutation | Argument | Input type |
|---|---|---|
updateRestaurant | data | RestaurantInput! |
For instance, the following example updates an existing document from the "Restaurants" content-type and give it a new name:
mutation UpdateRestaurant($documentId: ID!, $data: RestaurantInput!) {
updateRestaurant(
documentId: "bf97tfdumkcc8ptahkng4puo",
data: { name: "Pizzeria Amore" }
) {
documentId
name
}
}
If the Internationalization (i18n) feature is enabled for your content-type, you can create a document for a specific locale (see i18n documentation).
Update relations
You can update relational attributes by passing a documentId or an array of documentId (depending on the relation type).
For instance, the following example updates a document from the "Restaurant" content-type and adds a relation to a document from the "Category" content-type through the categories relation field:
mutation UpdateRestaurant($documentId: ID!, $data: RestaurantInput!) {
updateRestaurant(
documentId: "slwsiopkelrpxpvpc27953je",
data: { categories: ["kbbvj00fjiqoaj85vmylwi17"] }
) {
documentId
name
categories {
documentId
Name
}
}
}
Delete a document
To delete a document , pass its documentId:
mutation DeleteRestaurant {
deleteRestaurant(documentId: "a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl") {
documentId
}
}
If the Internationalization (i18n) feature is enabled for your content-type, you can delete a specific localized version of a document (see i18n documentation).
Mutations on media files
Currently, mutations on media fields use Strapi v4 id, not Strapi 5 documentId, as unique identifiers for media files.
Media fields mutations use files id. However, GraphQL API queries in Strapi 5 do not return id anymore. Media files id can be found:
-
either in the Media Library from the admin panel,
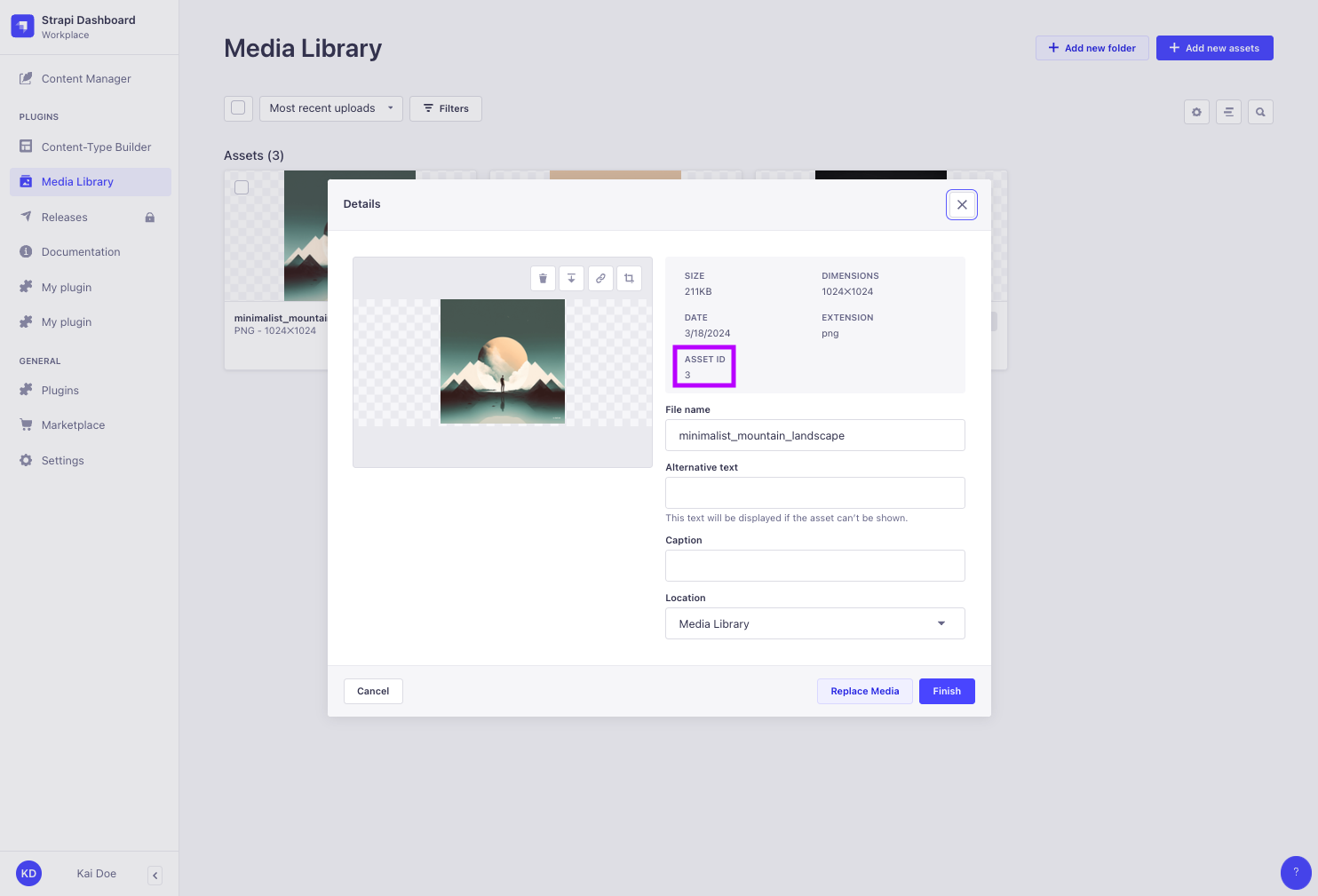

-
or by sending REST API
GETrequests that populate media files, because REST API requests currently return bothidanddocumentIdfor media files.
Update an uploaded media file
When updating an uploaded media file, pass the media's id (not its documentId) and the info object containing new content. The info argument will has an associated input type that is specific to media files.
For instance, if your Strapi project contains the "Restaurant" content-type, you will have the following:
| Mutation | Argument | Input type |
|---|---|---|
updateUploadFile | info | FileInfoInput! |
For instance, the following example updates the alternativeText attribute for a media file whose id is 3:
mutation Mutation($updateUploadFileId: ID!, $info: FileInfoInput) {
updateUploadFile(
id: 3,
info: {
alternativeText: "New alt text"
}
) {
documentId
url
alternativeText
}
}
If upload mutations return a forbidden access error, ensure proper permissions are set for the Upload plugin (see User Guide).
Delete an uploaded media file
When deleting an uploaded media file, pass the media's id (not its documentId).
mutation DeleteUploadFile($deleteUploadFileId: ID!) {
deleteUploadFile(id: 4) {
documentId # return its documentId
}
}
If upload mutations return a forbidden access error, ensure proper permissions are set for the Upload plugin (see User Guide).
Filters
Queries can accept a filters parameter with the following syntax:
filters: { field: { operator: value } }
Multiple filters can be combined together, and logical operators (and, or, not) can also be used and accept arrays of objects.
The following operators are available:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
eq | Equal |
ne | Not equal |
lt | Less than |
lte | Less than or equal to |
gt | Greater than |
gte | Greater than or equal to |
in | Included in an array |
notIn | Not included in an array |
contains | Contains, case sensitive |
notContains | Does not contain, case sensitive |
containsi | Contains, case insensitive |
notContainsi | Does not contain, case insensitive |
null | Is null |
notNull | Is not null |
between | Is between |
startsWith | Starts with |
endsWith | Ends with |
and | Logical and |
or | Logical or |
not | Logical not |
{
restaurants(
filters: {
averagePrice: { lt: 20 },
or: [
{ name: { eq: "Pizzeria" }}
{ name: { startsWith: "Pizzeria" }}
]}
) {
documentId
name
averagePrice
}
}
Sorting
Queries can accept a sort parameter with the following syntax:
- to sort based on a single value:
sort: "value" - to sort based on multiple values:
sort: ["value1", "value2"]
The sorting order can be defined with :asc (ascending order, default, can be omitted) or :desc (for descending order).
{
restaurants(sort: "name") {
documentId
name
}
}
{
restaurants(sort: "averagePrice:desc") {
documentId
name
averagePrice
}
}
{
restaurants(sort: ["name:asc", "averagePrice:desc"]) {
documentId
name
averagePrice
}
}
Pagination
Relay-style queries can accept a pagination parameter. Results can be paginated either by page or by offset.
Pagination methods can not be mixed. Always use either page with pageSize or start with limit.
Pagination by page
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
pagination.page | Page number | 1 |
pagination.pageSize | Page size | 10 |
{
restaurants_connection(pagination: { page: 1, pageSize: 10 }) {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
pageInfo {
page
pageSize
pageCount
total
}
}
}
Pagination by offset
| Parameter | Description | Default | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
pagination.start | Start value | 0 | - |
pagination.limit | Number of entities to return | 10 | -1 |
{
restaurants_connection(pagination: { start: 10, limit: 19 }) {
nodes {
documentId
name
}
pageInfo {
page
pageSize
pageCount
total
}
}
}
The default and maximum values for pagination.limit can be configured in the ./config/plugins.js file with the graphql.config.defaultLimit and graphql.config.maxLimit keys.
locale
The Internationalization (i18n) feature adds new features to the GraphQL API:
- The
localefield is added to the GraphQL schema. - GraphQL can be used:
Fetch all documents in a specific locale
To fetch all documents for a specific locale, pass the locale argument to the query:
query {
restaurants(locale: "fr") {
documentId
name
locale
}
}
{
"data": {
"restaurants": [
{
"documentId": "a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl",
"name": "Restaurant Biscotte",
"locale": "fr"
},
{
"documentId": "m9n8o7p6q5r4s3t2u1v0wxyz",
"name": "Pizzeria Arrivederci",
"locale": "fr"
},
]
}
}
Fetch a document in a specific locale
To fetch a documents for a specific locale, pass the documentId and the locale arguments to the query:
query Restaurant($documentId: ID!, $locale: I18NLocaleCode) {
restaurant(documentId: "a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl", locale: "fr") {
documentId
name
description
locale
}
}
{
"data": {
"restaurant": {
"documentId": "lviw819d5htwvga8s3kovdij",
"name": "Restaurant Biscotte",
"description": "Bienvenue au restaurant Biscotte!",
"locale": "fr"
}
}
}
Create a new localized document
The locale field can be passed to create a localized document for a specific locale (for more information about mutations with GraphQL, see the GraphQL API documentation).
mutation CreateRestaurant($data: RestaurantInput!, $locale: I18NLocaleCode) {
createRestaurant(
data: {
name: "Brasserie Bonjour",
description: "Description in French goes here"
},
locale: "fr"
) {
documentId
name
description
locale
}
Update a document for a specific locale
A locale argument can be passed in the mutation to update a document for a given locale (for more information about mutations with GraphQL, see the GraphQL API documentation).
mutation UpdateRestaurant($documentId: ID!, $data: RestaurantInput!, $locale: I18NLocaleCode) {
updateRestaurant(
documentId: "a1b2c3d4e5d6f7g8h9i0jkl"
data: {
description: "New description in French"
},
locale: "fr"
) {
documentId
name
description
locale
}
Delete a locale for a document
Pass the locale argument in the mutation to delete a specific localization for a document :
mutation DeleteRestaurant($documentId: ID!, $locale: I18NLocaleCode) {
deleteRestaurant(documentId: "xzmzdo4k0z73t9i68a7yx2kk", locale: "fr") {
documentId
}
}